This article describes how to connect to Microsoft SQL Server natively in both FactorySQL and FactoryPMI.
Background
Microsoft SQL Server is a popular robust relational database produced by Microsoft. FactorySQL and FactoryPMI can both connect to Microsoft SQL Server, however many users find difficulty in getting all of the settings and parameters correct. There are several different ways you can connect to Microsoft SQL Server (all using TCP/IP communication):
- Specifying a Port using Windows Authentication
- Specifying an Instance Name using Windows Authentication
- Specifying a Port using SQL Authentication
- Specifying an Instance Name using SQL Authentication
Before we begin, let's talk a little about how instances work. Microsoft SQL Server supports multiple instances of the database running concurrently on the same computer. Each instance has its own name and set of system and user databases that are not shared between instances. Applications, such as FactorySQL and FactoryPMI, can connect to each instance on a computer in much the same way they connect to databases running on different computers. Each instance gets assigned a dynamic TCP/IP port on startup that it will listen on for any incoming requests. Since the port is dynamic and the application will not know what the new port is, it must connect using the instance name.
If the communication is over TCP/IP and the application knows the instance name, how will the application find which port to communicate over?
The answer is the Microsoft SQL Server Browser Service. The Microsoft SQL Server Browser program runs as a Windows service and listens for all incoming requests for resources and provides information, such as the TCP/IP port, about each instance installed on the computer. Microsoft SQL Server Browser also contributes to the following actions:
- Browsing a list of available servers
- Connecting to the correct server instance
Step 1: Make Sure the Database has TCP/IP Enabled
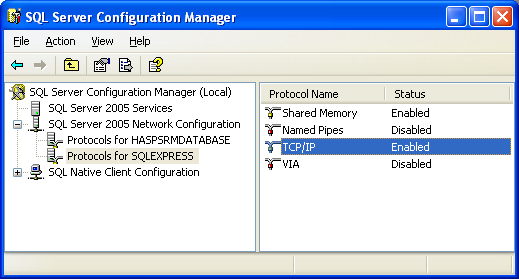
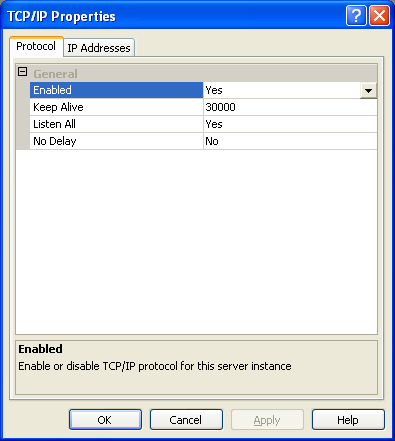
FactorySQL and FactoryPMI both connect using TCP/IP, so the first step is to make sure your database has TCP/IP enabled. To check, open up the SQL Server Configuration Manager from Start -> All Programs -> Microsoft SQL Server Version -> Configuration Tools -> SQL Server Configuration Manager. Once it is open, you will see all of the instances setup on that machine by expanding SQL Server Version Network Configuration. Find the database (or instance) you plan on using and click on it. To the right you will see all of the protocols the database supports. One of the protocols is TCP/IP. Make sure the status next to TCP/IP is set to Enabled. If not, double click on TCP/IP and choose Yes from the drop-down next to Enabled and press OK.
Step 2: Make Sure Microsoft SQL Server Browser is Running
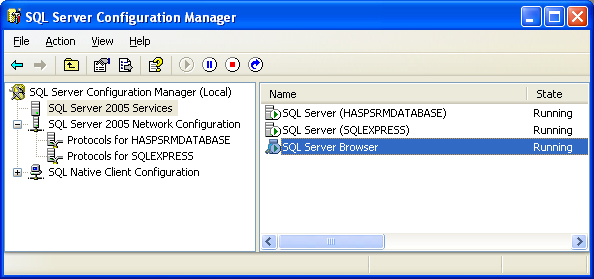
If you ARE connecting to your database using a NAMED INSTANCE you must make sure that the Microsoft SQL Server Browser is running. As mentioned earlier, the Microsoft SQL Server Browser translates the instance name to a TCP/IP port in order for your application (FactorySQL or FactoryPMI) to connect to it. To check open up the SQL Server Configuration Manager from Start -> All Programs -> Microsoft SQL Server Version -> Configuration Tools -> SQL Server Configuration Manager. Once it is open, select the SQL Server Version Services section. To the right you will see all of the services installed. One of the services is SQL Server Browser. Make sure this service is in fact running. If the service is not running, right click and select Start.
Step 3: Make Sure Microsoft SQL Server Allows SQL Authentication
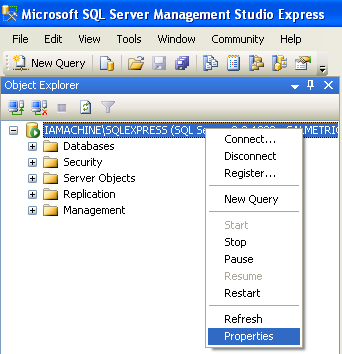
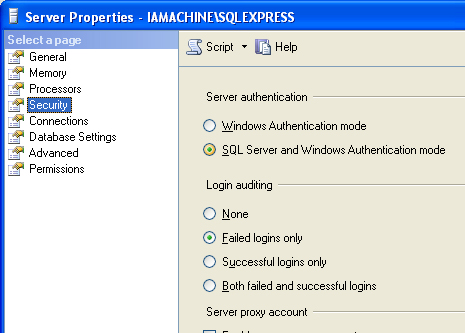
If you ARE using SQL authentication to connect to your database make sure the database allows for this type of connection. To check open the SQL Server Management Studio from Start -> All Programs -> Microsoft SQL Server Version -> SQL Server Management Studio. Once open and connected to your database, right click on the top level database in the Object Explorer and select Properties. Once the Server properties window is open, select Security on the left hand side. Once open verify that SQL Server and Windows Authentication mode is selected. If not, select it and press OK. You will have to restart the SQL Server Windows service for this setting to take effect.
FactorySQL: How to Connect to Microsoft SQL Server
To connect to a Microsoft SQL Server database, open up the FactorySQL Frontend from Start -> All Programs -> Inductive Automation -> FactorySQL -> FactorySQL Frontend. Once open, select Settings from the file menu and click on Data Connection Settings. In this section we can create stored connections to any SQL database natively or using a DSN connection. If you are connecting to a database natively, each driver type (MySQL, SQL Server, etc) uses an XML file located in C:\Program Files\Inductive Automation\FactorySQL\database that describes how FactorySQL will connect. By looking in that directory you may find multiple SQL Server XML files, which are separate Translators for that specific driver type. These translators differ in the Connection String that FactorySQL will use to connect to your database. For example, the SQL Server Windows Auth translator allows you to connect using Windows authentication, which is one of the ways you can connect to Microsoft SQL Server. As we mentioned earlier, there are several ways to connect to Microsoft SQL Server and here are the basic XML files for each method:
- Specifying a Port using Windows Authentication
- Specifying an Instance Name using Windows Authentication
- Automatic translator - Specifying a Port using SQL Authentication
- Specifying an Instance Name using SQL Authentication
- Only for SQL Server 2000 - For SQL Server 2000
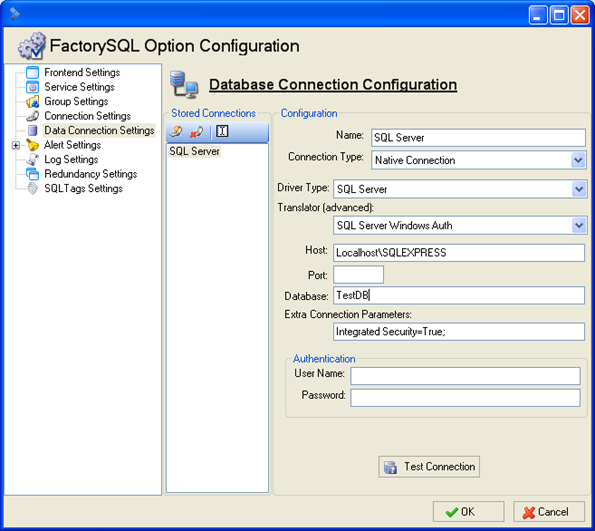
Let's take the most common, specifying an Instance Name using Windows Authentication. Now, create a new connection and give it a name, such as SQL Server. Select Native Connection as the connection type. Select SQL Server as the Driver type to use the Microsoft SQL Server driver that comes with FactorySQL. With this driver we have multiple translators to use, shown above, so select the SQL Server Windows Auth or SQL Server Windows Auth Instance (from this example) as the Translator (advanced). For the host, type in the host name and the instance name, for example localhost\SQLEXPRESS. The port will remain blank since we are not using the port. Type in the database name in the Database field. This is the name of the database you want to connect to in the specified instance. Type in Integrated Security=true; into the Extra Connection Parameters if it is not already there. Leave the username and password field blank and that is it. Press the Test Connection to verify communication.
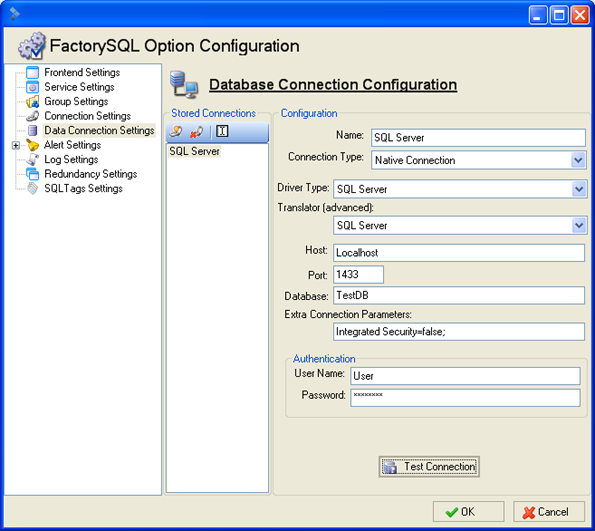
Let's take the second most common, specifying a Port using SQL Authentication. Now, create a new connection and give it a name, such as SQL Server. Select Native Connection as the connection type. Select SQL Server as the Driver type to use the Microsoft SQL Server driver that comes with FactorySQL. With this driver we have multiple translators to use, shown above, so select the SQL Server or Automatic as the Translator (advanced). For the host, type in the host name, for example localhost. Specify the port which is 1433 by default. Type in the database name in the Database field. This is the name of the database you want to connect to. Type in Integrated Security=false; into the Extra Connection Parameters if it is not already there. Type in your username and password and that is it. Press the Test Connection to verify communication.
FactoryPMI: How to Connect to Microsoft SQL Server
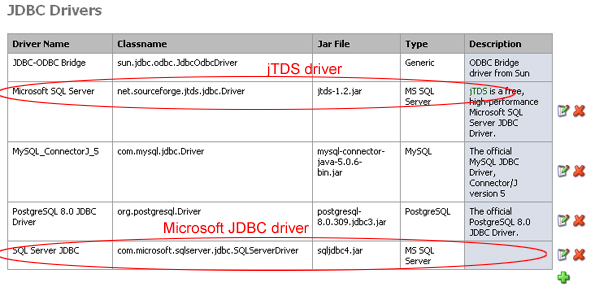
To connect to a Microsoft SQL Server database, open up the FactoryPMI Configuration Page from Start -> All Programs -> Inductive Automation -> FactoryPMI -> Configuration Page. Once open, log in and select Drivers under Datasources. There are two drivers that can connect to Microsoft SQL Server, jTDS and Microsoft's SQL Server JDBC. Due to licensing restrictions we used to ship FactoryPMI with the jTDS driver. However, one can download and use the most current Microsoft SQL Server JDBC driver. We recommend you use Microsoft's JDBC driver instead of the jTDS and this article will show you how to connect using Microsoft's driver.If you do not already have Microsoft's JDBC driver please follow the instructions below.
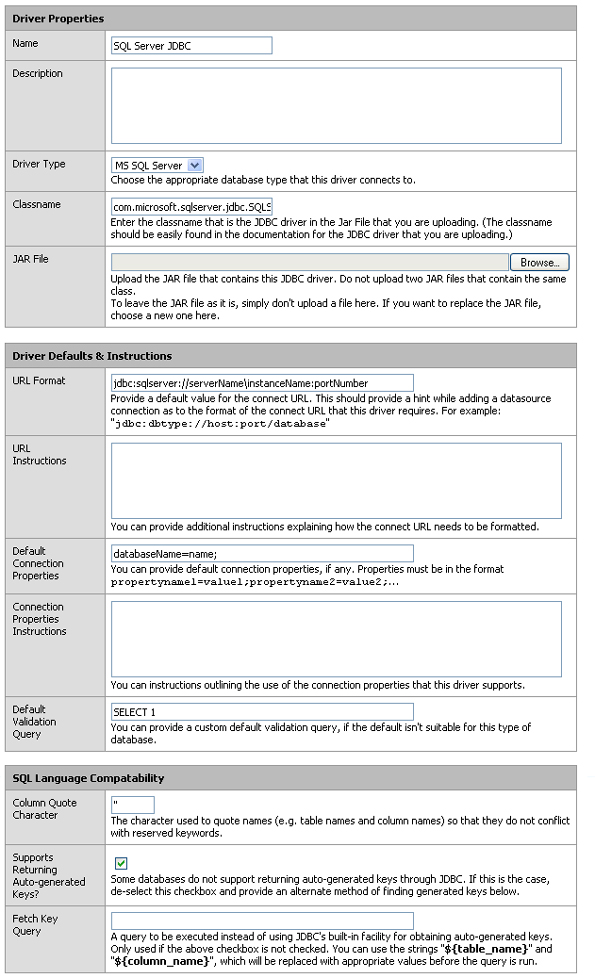
First download the newest Microsoft SQL Server JDBC driver from here: http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyID=99b21b65-e98f-4a61-b811-19912601fdc9&displaylang=en. Once you extract it you will find 2 jar files sqljdbc.jar and sqljdbc4.jar that we will use later. First, copy the appropriate sqljdbc_auth.dll from the auth/architecture directory into C:\Program Files\Inductive Automation\FactoryPMI\lib and restart your FactoryPMI Gateway. Once restarted, open the Gateway configuration page once more and go back to Datasources -> Drivers section. Press the add icon to add a new driver. Use the following diagram as your parameters and press Add Driver:
Name: SQL Server JDBC
Description:
Driver Type: MS SQL Server
Classname: com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver
Jar File: If your FactoryPMI Gateway is running on Java 5, find sqljdbc.jar. If your FactoryPMI Gateway is running Java 6, find sqljdbc4.jar.
URL Format: jdbc:sqlserver://serverName\instanceName:portNumber
URL Instructions:
Default Connection Properties: databaseName=name;
Connection Properties Instructions:
Default Validation Query: SELECT 1
Column Quote Character: "
Supports Returning Auto-Generated Keys?: Check
Fetch Key Query:
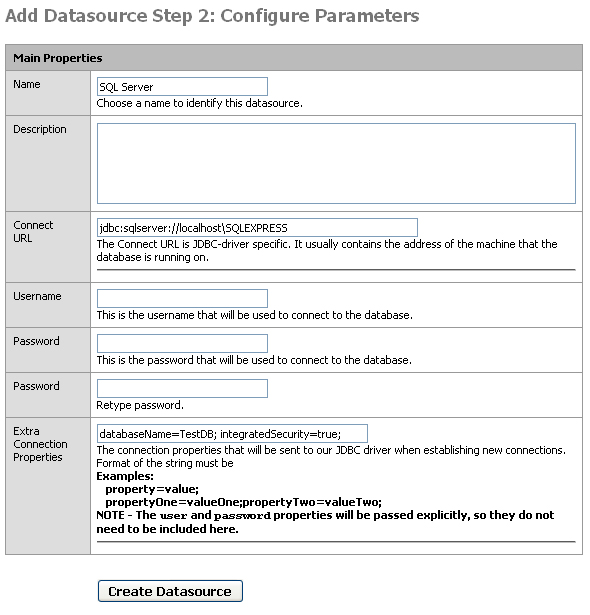
Once the JDBC driver is added we can create a new connection. Let's take the most common way to create a connection, specifying an Instance Name using Windows Authentication. Select Datasources -> Connections and press the add icon to create a new connection. Select SQL Server JDBC as the JDBC driver from the drop-down and press Next. Give it a name, such as SQL Server. Edit the Connect URL to specify your database host and instance name, for example jdbc:sqlserver://localhost\SQLEXPRESS. Leave the username and password fields blank. In the Extra Connection Properties specify the database name you want to connect to and use integrated security, for example databaseName=TestDB; integratedSecurity=true;. Press Create Datasource and the background of the connection will let you know if it is connected.
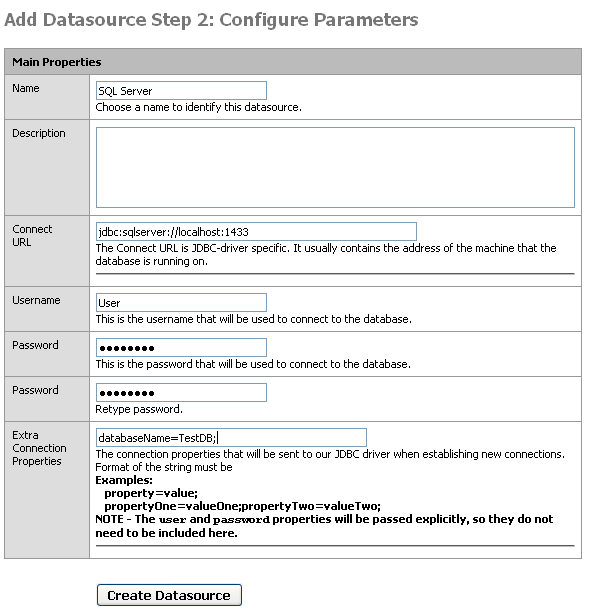
Let's take the second most common way to create a connection, specifying a Port using SQL Authentication. Select Datasources -> Connections and press the add icon to create a new connection. Select SQL Server JDBC as the JDBC driver from the drop-down and press Next. Give it a name, such as SQL Server. Edit the Connect URL to specify your database host and port, for example jdbc:sqlserver://localhost:1433. Enter in your username and password. In the Extra Connection Properties specify the database name you want to connect to, for example databaseName=TestDB;. Press Create Datasource and the background of the connection will let you know if it is connected.
Summary
The settings for both FactoryPMI and FactorySQL can be combined to connect using Windows Auth and Port and SQL Auth and Instance. The two examples above show how to use the two most common methods. As always, if you have any questions or are still having problems getting connected to SQL Server call us at (800) 266-7798.